I wish to be called back
Fill out the form below and we will call you back at the times indicated :
Fill out the form below and we will call you back at the times indicated :
—
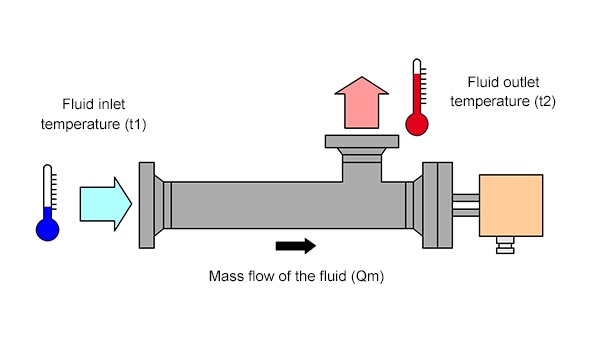
Calculation of the power required to raise the temperature of a fluid (liquid or gas), in a single pass, circulating continuously in a heater ou duct heater.
The temperature difference between the inlet ant outlet is quaranteed for a set system after operating for several minutes. Upon start-up, since all equipment, heater body, heater case, heating tubes, are at room temperature, it is not possible to instantaneously obtain the desired outlet temperature of the fluid.
This calculation is not applicable in the case where the fluid is gradually heated by successive passes through the heater.
—
—
– Heating power : Pch (kW)
– Mass flow rate : Qm (kg/h)
– Specific heat of fluid : Cp (kcal/kg × °C)
– Inlet temperature : t1 (°C)
– Required outlet temperature : t2 (°C)
– 1,2 : Safety coefficient linked to our manufacturing tolerances and variations in network power
—
Pch = (Qm × Cp ×(t2 − t1) × 1,2) ÷ 860
—
—
1/ Calculation of the mass flow rate for a liquid :
– Mass flow rate : Qm (kg/h)
– Volume flow rate : Qv (dm3/h ou l/h)
– Density of the liquid : ρ (kg/dm3)
—
Qm = Qv × ρ
ρ / Cp values for a few liquids :
Water : 1 / 1
Mineral oil : 0,9 / 0,5
Bitumen : 1,1 / 0,58
Acetic acid : 1,1 / 0,51
Hydrochloric acid : 1,2 / 0,6
Nitric acid : 1,5 / 0,66
—
—
2/ Calculation of the mass flow rate for a gas :
a/ volume flow rate given in Nm3/h :
– Mass flow rate : Qm (kg/h)
– Volume flow rate : Qv (Nm3/h)
– Volume flow rate of the gas at
atmospheric pressure and at 0 °C : ρ (kg/m3)
—
Qm = Qv × ρ
—
b/ Volume flow rate given in m3/h :
– Mass flow rate : Qm (kg/h)
– Volume flow rate : Qv (m3/h)
– Service pressure at heater inlet : p (bar rel.)
– Inlet temperature of the gas : t1 (°C)
– Volume flow rate of the gas at
atmospheric pressure and at 0 °C : ρ (kg/m3)
—
Qm = (Qv × ρ × (p + 1) × 273) ÷ (273 + t1)
ρ / Cp values for a few gases :
Acetylene : 1,17 / 0,40
Dry air : 1,29 / 0,24
Ammonia : 0,77 / 0,48
Nitrogen : 1,25 / 0,25
Chlorine : 3,2 / 0,12
Natural gas : 0,75 / 0,50
Carbon dioxide : 2 / 0,20
Hydrogen : 0,09 / 3,4
Oxygen : 1,42 / 0,22
Steam : 0,59 / 0,49
—
—
—