I wish to be called back
Fill out the form below and we will call you back at the times indicated :
Fill out the form below and we will call you back at the times indicated :
—
The power to be installed in order to raise the temperature over a given time of a volume of liquid contained in a tank is the result of 2 calculations: The calculation of the power to raise the temperature of the liquid (Pch) and the calculation of the heat loss (Pth).
—
Power to be installed (kW) = Heating power (Pch) + Heat loss (Pth)
—
—
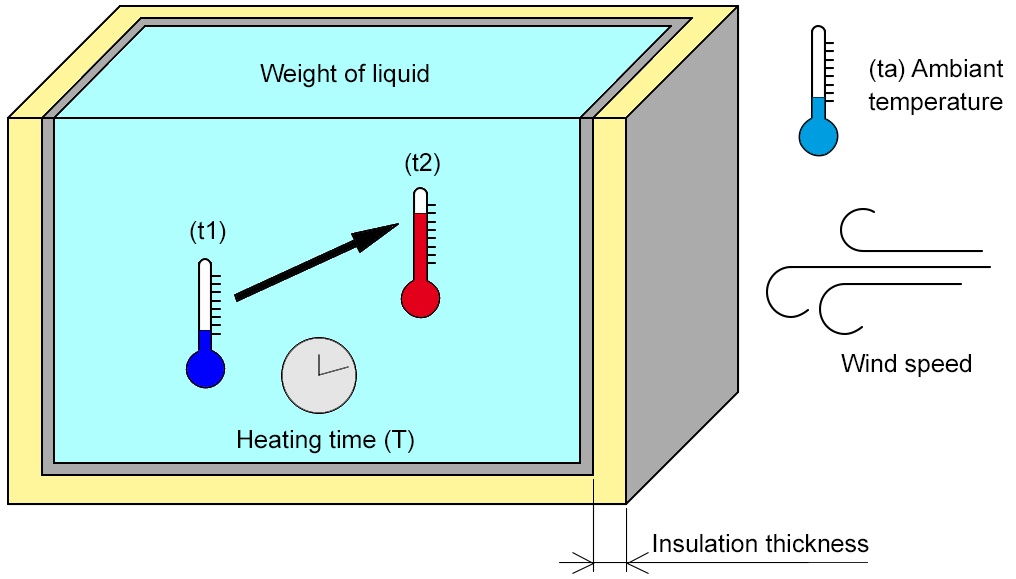
1 / Calculation of the power required to raise the temperature of a volume of liquid:
—
– Heating power : Pch (kW)
– Weight of liquid : M (kg)
– Specific heat of liquid : Cp (kcal/kg×°C)
– Starting temperature : t1 (°C)
– Required end temperature : t2 (°C)
– Heating time : T (h)
– 1,2 : Safety coefficient linked to our manufacturing tolerances and variations in network power
—
Pch = (M × Cp × (t2 − t1) × 1,2) ÷ (860 × T)
—
—
—
a/ Calculation of the mass of liquid to be heated :
– Weight of liquid : M (kg)
– Volume of liquid to be heated : V (dm3 ou litre)
– Density of the liquid : ρ (kg/dm3)
—
M = V × ρ
—
ρ / Cp values for a few liquids :
Water : 1 / 1
Mineral oil : 0,9 / 0,5
Bitumen : 1,1 / 0,58
Acetic acid : 1,1 / 0,51
Hydrochloric acid : 1,2 / 0,6
Nitric acid : 1,5 / 0,66
—
b/ Calculation of the volume of liquid :
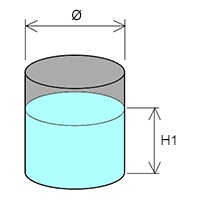
In a cylindrical tank :
– Volume of tank : V (dm3)
– Diameter of tank : ∅ (dm)
– Height of liquid : H1 (dm)
V = π × (∅² ÷ 4) × H1
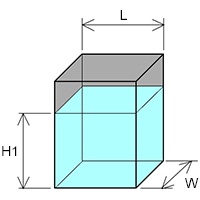
In a rectangular tank :
– Volume of tank : V (dm3)
– Length of tank : L (dm)
– Width of tank : W (dm)
– Height of liquid : H1 (dm)
V = L × W × H1
2 / Calculation of the power required to compensate for heat loss :
– Heat loss : Pth (kW)
– Exchange surface area of the tank : S (m2)
– Required end temperature : t2 (°C)
– A temperature : ta (°C)
– Exchange coefficient : K (kcal/h × m2 × °C)
– 1,2 : Safety coefficient linked to our manufacturing tolerances and variations in network power
Pth = (S × (t2 – ta) × K × 1,2) ÷ 860
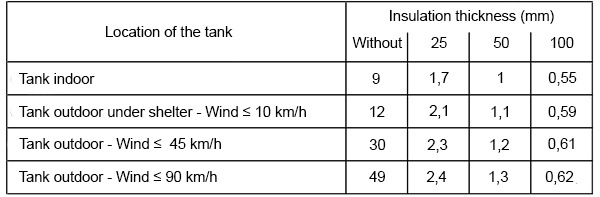
Exchange coefficient K as a function of the wind speed and insulation thickness :
a/ Calculation of the exchange surface area of the tank :
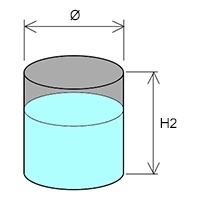
Surface area of a cylindrical tank :
– Surface area of the tank : S (m2)
– Diameter of tank : ∅ (m)
– Height of the tank : H2 (m)
S = (π × (∅² ÷ 4)) + (π × ∅ × H2)
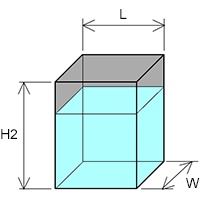
Surface area of a rectangular tank :
– Surface area of the tank : S (m2)
– Length of tank : L (m)
– Width of tank : W (m)
– Height of the tank : H2 (m)
S = ((L + W ) × H2 × 2) + (L × W)
—